Mary Hall Reno - Research Interests
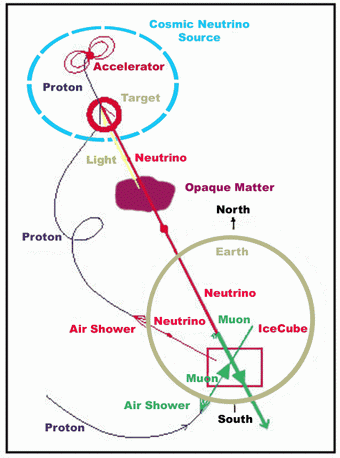 My research over the past fifteen years has concentrated on aspects of neutrino physics, generally in the high energy regime with
astroparticle physics connections. In this schematic figure, neutrinos are
produced in astrophysical sources and in the Earth's atmosphere. Aspects of muon interactions with matter are relevant to neutrino detection, as are oscillation effects for neutrinos in transit to the Earth, and in the Earth itself.
My research over the past fifteen years has concentrated on aspects of neutrino physics, generally in the high energy regime with
astroparticle physics connections. In this schematic figure, neutrinos are
produced in astrophysical sources and in the Earth's atmosphere. Aspects of muon interactions with matter are relevant to neutrino detection, as are oscillation effects for neutrinos in transit to the Earth, and in the Earth itself.
Much of my research is done with students and/or in collaboration with Prof. Ina Sarcevic at the University of Arizona.
Among my interests are:
- The neutrino cross section at ultrahigh energies. Actual measurements of the neutrino nucleon cross section are done to about 500 GeV neutrino energies. For the astroparticle physics observations, neutrino cross sections many orders of magnitude higher are required. High energy extrapolations involve small-x QCD, and may offer opportunities for signals of new physics.
-
Mass/low Q corrections to the neutrino cross section. These corrections include target mass corrections, kinematic corrections for tau lepton production and the non-perturbative low Q nucleon structure functions.
-
Neutrino fluxes from conventional physics processes with cosmic ray interactions in the atmosphere, including charmed particle production. This is another small-x (but now lower Q) QCD process.
-
Neutrino fluxes from conventional physics processes in astrophysical sources, where the density and magnetic field conditions are much different than in the atmosphere, but the physics is the same.
-
Neutrinos from dark matter annihilation and dark matter decay in the galactic halo and from density enhancements in the core of the Earth or Sun.
-
With members of our experimental group, I have joined DUNE, with a personal interest in the Monte Carlo simulation of the neutrino cross section.
Figure credit: NSF and physorg.com
Recent students and their projects
-
Weidong Bai - current student, working on a project related to the tau neutrino flux that will be a by-product of the SHiP (CERN) effort to search for hidden particles.
-
Minh Vu Luu - current student, working on a project on the dipole approach to electromagnetic structure functions. Our first paper describes our work on extracting an
approximate dipole cross section from recent parameterizations of the structure
function F2. He is currently focusing on tau lepton energy loss, which depends in part on the structure function at small-x.
-
Yu Seon Jeong - worked a project on quark mass corrections to the neutrino cross section at high energies, where the flavor scheme of the QCD corrections at next-to-leading order were evaluated. Another project has been an update of the tau neutrino and antineutrino nucleon scattering cross section, at next-to-leading order, for neutrino energies between 10 GeV and 10 TeV. Dr. Jeong graduated in May 2011, then joined Yonsei University in Korea as a postdoc.
-
Alexander Bulmahn - an update of the lepton pair production cross section and energy distribution for muons producing lepton pairs as they pass through materials like ice or rock. While rarely occuring, muons can produce tau pairs as well. Dr. Bulmahn (PhD in May 2010) is an instructor at the University of Montana.
 My research over the past fifteen years has concentrated on aspects of neutrino physics, generally in the high energy regime with
astroparticle physics connections. In this schematic figure, neutrinos are
produced in astrophysical sources and in the Earth's atmosphere. Aspects of muon interactions with matter are relevant to neutrino detection, as are oscillation effects for neutrinos in transit to the Earth, and in the Earth itself.
My research over the past fifteen years has concentrated on aspects of neutrino physics, generally in the high energy regime with
astroparticle physics connections. In this schematic figure, neutrinos are
produced in astrophysical sources and in the Earth's atmosphere. Aspects of muon interactions with matter are relevant to neutrino detection, as are oscillation effects for neutrinos in transit to the Earth, and in the Earth itself.